The Impact of Indoor Air Quality on Health
The Impact of Indoor Air Quality on Health
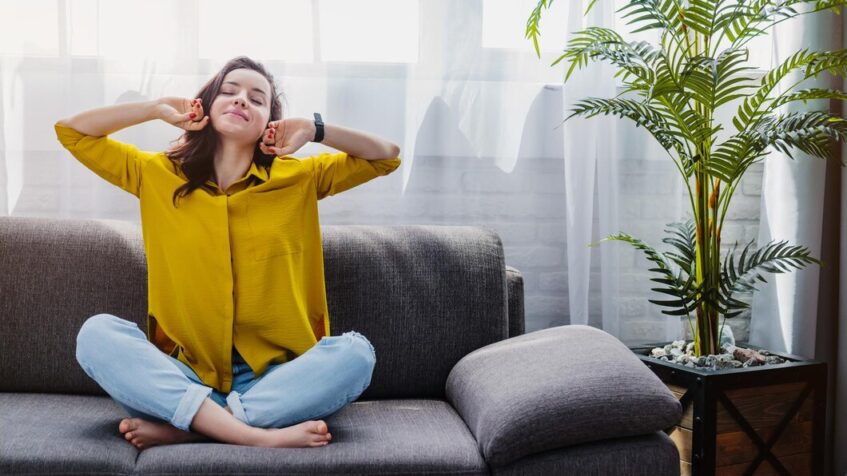
Health is undoubtedly one of our most precious assets, yet often overlooked is the vital role that indoor air quality plays in maintaining it. The air we breathe within the confines of our homes and workplaces can significantly impact our overall well-being. From respiratory issues to cognitive function, the quality of indoor air can influence a myriad of health factors. In this blog, we delve into the profound impact of indoor air quality on our health, exploring its implications and offering insights into fostering a healthier indoor environment.
Understanding Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality (IAQ) refers to the condition of the air within buildings, including homes, offices, schools, and other indoor environments. It encompasses various factors such as temperature, humidity, pollutants, and ventilation. Poor IAQ can result from the presence of pollutants like dust, mold, pet dander, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and tobacco smoke.
These pollutants can lead to health issues ranging from allergies and asthma to more severe respiratory conditions and even cardiovascular problems. Understanding IAQ is crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor environment and mitigating the risks associated with poor air quality.
Respiratory Health Concerns
Poor indoor air quality can have significant implications for respiratory health. Exposure to pollutants such as particulate matter, allergens, and VOCs can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and pollen are common allergens found indoors that can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory symptoms.
Additionally, long-term exposure to indoor air pollutants may increase the risk of developing respiratory infections and even lung cancer. Ensuring good indoor air quality through proper ventilation and air filtration is essential for reducing respiratory health concerns and promoting overall well-being.
Cognitive Impact of Poor Air Quality
In addition to its effects on respiratory health, poor indoor air quality can also impact cognitive function. Research suggests that exposure to indoor air pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and fine particulate matter, can impair cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and decision-making. These pollutants may enter the bloodstream and reach the brain, where they can cause inflammation and oxidative stress, leading to cognitive decline over time.
Furthermore, inadequate ventilation in indoor spaces can result in a buildup of carbon dioxide, which can cause drowsiness and reduce cognitive performance. Improving indoor air quality is essential for maintaining optimal cognitive function and productivity.
Allergens and Irritants in Indoor Air
Indoor air can harbor a variety of allergens and irritants that can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory symptoms in sensitive individuals. Common indoor allergens include dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, pollen, and cockroach droppings. Exposure to these allergens can lead to symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, wheezing, nasal congestion, and skin rashes.
Additionally, indoor air may contain irritants such as tobacco smoke, cooking fumes, and household cleaning products, which can exacerbate respiratory issues and cause discomfort. Minimizing exposure to indoor allergens and irritants through proper ventilation, air filtration, and regular cleaning is essential for reducing allergic reactions and improving indoor air quality.
Sources of Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution can originate from various sources within the home or workplace. Common sources include combustion appliances such as gas stoves, fireplaces, and heaters, which can emit carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and other harmful gasses when not properly vented. Tobacco smoke is another significant source of indoor air pollution, containing numerous toxic chemicals that can linger in indoor environments long after smoking has ceased.
Additionally, building materials, furniture, and household products can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants into the air, contributing to poor indoor air quality. Understanding these sources is crucial for effectively mitigating indoor air pollution and safeguarding health.
Health Risks of Mold and Mildew
Mold and mildew are common indoor air pollutants that thrive in damp, humid environments. These fungi can grow on various surfaces, including walls, ceilings, floors, and even household items like carpets and upholstery. Exposure to mold and mildew can pose significant health risks, particularly for individuals with allergies, asthma, or weakened immune systems. Inhalation of mold spores and their byproducts can trigger allergic reactions, respiratory symptoms, and exacerbate existing health conditions.
Prolonged exposure to mold and mildew may also lead to more severe respiratory infections and inflammation of the airways. Preventing and addressing moisture issues in indoor spaces is essential for controlling mold growth and minimizing associated health risks.
Effects of Chemical Pollutants
Chemical pollutants present in indoor air can have various adverse effects on human health. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are emitted by products such as paints, solvents, cleaning agents, and building materials, can cause short-term health effects such as headaches, dizziness, and irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat. Long-term exposure to high levels of VOCs may increase the risk of developing respiratory and neurological disorders, as well as certain cancers.
Additionally, exposure to formaldehyde—a common indoor air pollutant found in pressed wood products, carpets, and upholstery—has been linked to respiratory symptoms, allergic reactions, and carcinogenic effects. Minimizing exposure to chemical pollutants through proper ventilation, source control, and use of low-emission products is essential for protecting indoor air quality and human health.
Importance of Ventilation Systems
Ventilation systems play a crucial role in maintaining good indoor air quality by continuously exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. Proper ventilation helps dilute indoor air pollutants, including carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and airborne particles, reducing their concentrations to levels that are safe for occupants.
Additionally, ventilation helps control indoor humidity levels, which can help prevent mold and mildew growth. Inadequate ventilation can lead to a buildup of indoor pollutants, resulting in poor air quality and potential health risks. Therefore, investing in effective ventilation systems is essential for promoting a healthy indoor environment and ensuring the well-being of building occupants.
Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality requires a multifaceted approach that addresses various sources of pollution and promotes proper ventilation and filtration. Strategies for enhancing indoor air quality include:
- Source Control: Minimize or eliminate sources of indoor air pollutants, such as tobacco smoke, combustion appliances, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation by using mechanical ventilation systems or opening windows and doors to allow fresh outdoor air to circulate indoors.
- Air Filtration: Use high-efficiency air filters in HVAC systems to capture airborne particles and allergens, and consider portable air purifiers for additional filtration.
- Humidity Control: Maintain indoor humidity levels between 30-50% to prevent mold and mildew growth and reduce the spread of airborne viruses.
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum carpets and upholstery regularly, and clean surfaces with non-toxic cleaning products to remove dust, dirt, and other pollutants.
- Indoor Plants: Incorporate indoor plants known for their air-purifying properties, such as spider plants and peace lilies, to help remove pollutants and improve air quality.
Indoor Air Quality Monitoring
Indoor air quality monitoring involves the measurement and assessment of various pollutants present in indoor environments to ensure that air quality meets health and safety standards. Monitoring indoor air quality helps identify potential sources of pollution, assess the effectiveness of ventilation and filtration systems, and determine the overall healthfulness of indoor environments. Monitoring parameters may include levels of carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, humidity, and temperature.
Continuous monitoring with sensors or periodic assessments by professionals can provide valuable insights into indoor air quality and help inform decisions regarding ventilation, filtration, and other strategies for improving air quality. By monitoring indoor air quality, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their health and well-being in indoor environments.
Health Benefits of Clean Air
Clean air is not merely a luxury; it’s a fundamental necessity for good health. Breathing in fresh air devoid of pollutants can have a profound impact on our well-being. It enhances respiratory function, minimizing the risk of infections and alleviating symptoms of allergies and asthma. Moreover, clean air supports cardiovascular health, reducing the likelihood of heart disease and stroke.
Beyond physical health, it boosts cognitive function, elevates mood, and enhances sleep quality. By prioritizing clean air and improving indoor air quality, individuals can unlock a plethora of health benefits, paving the way for a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Impact of Indoor Air Quality on Children
Children are particularly vulnerable to the effects of indoor air pollution due to their developing respiratory and immune systems, higher breathing rates, and increased time spent indoors. Poor indoor air quality can have significant implications for children’s health, leading to respiratory issues such as asthma and allergies, as well as developmental problems and cognitive impairments.
Exposure to indoor air pollutants during childhood can also increase the risk of long-term health problems, including respiratory diseases and cardiovascular conditions. Creating a healthy indoor environment is crucial for protecting children’s health and ensuring their optimal growth and development.
Creating a Healthy Indoor Environment
Creating a healthy indoor environment involves implementing various strategies to minimize exposure to indoor air pollutants and promote good indoor air quality. Key steps for creating a healthy indoor environment include:
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation by opening windows, using exhaust fans, or installing mechanical ventilation systems to circulate fresh outdoor air indoors.
- Air Filtration: Use high-efficiency air filters in HVAC systems to remove airborne particles and allergens, and consider portable air purifiers for additional filtration.
- Source Control: Minimize or eliminate sources of indoor air pollution, such as tobacco smoke, household chemicals, and mold and mildew.
- Humidity Control: Maintain indoor humidity levels between 30-50% to prevent mold and mildew growth and reduce the spread of airborne viruses.
- Regular Cleaning: Vacuum carpets and upholstery regularly, and clean surfaces with non-toxic cleaning products to remove dust, dirt, and other pollutants.
- Indoor Plants: Incorporate indoor plants known for their air-purifying properties, such as spider plants and peace lilies, to help remove pollutants and improve air quality.
The impact of indoor air quality on health cannot be overstated. As we’ve explored, clean air is essential for respiratory, cardiovascular, and cognitive well-being, among other health benefits. At Cool Factory, Inc, we understand the significance of maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
If you’re concerned about the air quality in your home or workplace, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our team of experts in Sterling, VA, is dedicated to providing solutions tailored to your indoor air quality needs. Contact us today at (703) 713-5113 to learn more and take the first step towards breathing cleaner, healthier air.